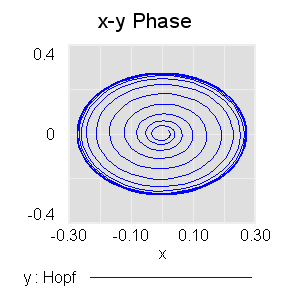
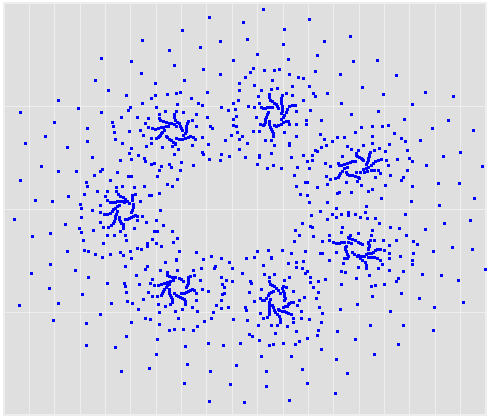
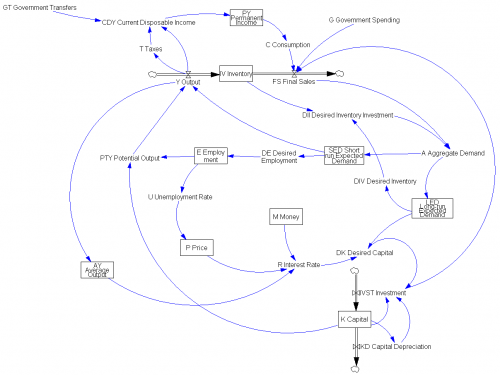
This is John Sterman’s model of long waves (long-duration economic cycles), driven by capital accumulation dynamics. This version is replicated from a JEBO article,
There’s some interesting related literature (including other economic models in this library). From Sterman’s publications list:
STERMAN, J. D. & MOSEKILDE, E. (1994) Business Cycles and Long Waves: A Behavioral, Disequilibrium Perspective. IN SEMMLER, W. (Ed.) Business Cycles: Theory and Empirical Methods. Boston, Kluwer Academic Publishers.
STERMAN, J. D. (1994) The Economic Long Wave: Theory and Evidence. IN SHIMADA, T. (Ed.) An Introduction to System Dynamics. Tokyo.
STERMAN, J. D. (2002) A Behavioral Model of the Economic Long Wave. IN EARL, P. E. (Ed.) The Legacy of Herbert Simon in Economic Analysis. Cheltenham, UK, Edward Elgar.
STERMAN, J. D. (1985) An Integrated Theory of the Economic Long Wave. Futures, 17, 104-131.
RASMUSSEN, S., MOSEKILDE, E. & STERMAN, J. D. (1985) Bifurcations and Chaotic Behavior in a Simple Model of the Economic Long Wave. System Dynamics Review, 1, 92-110.
STERMAN, J. D. (1983) The Long Wave. Science, 219, 1276.
KAMPMANN, C., HAXHOLDT, C., MOSEKILDE, E. & STERMAN, J. D. (1994) Entrainment in a Disaggregated Economic Long Wave Model. IN LEYDESDORFF, L. & VAN DEN BESSELAAR, P. (Eds.) Evolutionary Economics and Chaos Theory. London, Pinter.
MOSEKILDE, E., LARSEN, E. R., STERMAN, J. D. & THOMSEN, J. S. (1993) Mode Locking and Nonlinear Entrainment of Macroeconomic Cycles. IN DAY, R. & CHEN, P. (Eds.) Nonlinear Economics and Evolutionary Economics. New York, Oxford University Press.
MOSEKILDE, E., THOMSEN, J. S. & STERMAN, J. D. (1992) Nonlinear Interactions in the Economy. IN HAAG, G., MÜLLER, U. & TROITZSCH, K. (Eds.) Economic Evolution and Demographic Change. Berlin, Springer Verlag.
THOMSEN, J. S., MOSEKILDE, E. & STERMAN, J. D. (1991) Hyperchaotic Phenomena in Dynamic Decision Making. IN SINGH, M. G. & TRAVÉ-MASSUYÈS, L. (Eds.) Decision Support Systems and Qualitative Reasoning. Amsterdam, Elsevier Science Publishers.
THOMSEN, J. S., MOSEKILDE, E., LARSEN, E. R. & STERMAN, J. D. (1991) Mode-Locking and Chaos in a Periodically Driven Model of the Economic Long Wave. IN EBELING, W. (Ed.) Models of Self Organization in Complex Systems. Berlin, Akademie Verlag.
STERMAN, J. D. (1988) Nonlinear Dynamics in the World Economy: The Economic Long Wave. IN CHRISTIANSEN, P. & PARMENTIER, R. (Eds.) Structure, Coherence, and Chaos in Dynamical Systems. Manchester, Manchester University Press.
STERMAN, J. D. (1987) Debt, Default, and Long Waves: Is History Relevant? IN BOECKH, A. (Ed.) The Escalation in Debt and Disinflation: Prelude to Financial Mania and Crash? Montreal, BCA Publications.
STERMAN, J. D. (1987) An Integrated Theory of the Economic Long Wave. IN WANG, Q., SENGE, P., RICHARDSON, G. P. & MEADOWS, D. H. (Eds.) Theory and Application of System Dynamics. Beijing, New Times Press.
STERMAN, J. D. (1987) The Economic Long Wave: Theory and Evidence. IN VASKO, T. (Ed.) The Long Wave Debate. Berlin, Springer Verlag.
RASMUSSEN, S., MOSEKILDE, E. & STERMAN, J. D. (1987) Bifurcations and Chaotic Behavior in a Simple Model of the Economic Long Wave. IN WANG, Q., SENGE, P., RICHARDSON, G. P. & MEADOWS, D. H. (Eds.) Theory and Application of System Dynamics. Beijing, New Times Press.
The long wave model was the guine pig for Kampmann’s interesting ’96 conference paper that combined a graph-theoretic identification of a set of feedback loops having independent gains with eigenvalue analysis,
There also used to be a nifty long wave game, programmed on NEC minicomputers (32k memory?), but I’ve lost track of it. I’d be interested to here of a working version.